Container > NHN Container Service (NCS) > Overview
NCS is a service that provides environments for running containers. You can use this service to run containers without configuring container execution environments, such as a VM Instance and Kubernetes.
NCS Characteristics
- You can run container images stored in the public/private container registry.
- Because a container is connected to the user VPC, it can communicate with any IaaS resources, such as Instances, Load balancers, and Online NAS, etc. and take advantage of the networking capabilities provided by VPC.
- Containers can utilize Online NAS as Volume, or use NFSv3 Mount Points accessible from VPC as Volume.
- You can configure containers that use GPUs.
- You can connect Load Balancer to containers. You can expose container services outside through the created Floating IP and Domain.
- You can monitor the CPU, Memory, network transmission and reception, and storage of containers.
- Zero-downtime deployment is possible through the rolling update method.
- You can schedule container execution by setting up a time-based schedule.
- You can use the files uploaded to Object Storage or confidential data stored in Secure Key Manager by mounting them on container directories.
- An internal load balancer that is only available in NCS is provided.
- You can auto-register container IPs to Private DNS.
Configuration and Terms
The following image shows an example of NCS service configuration.
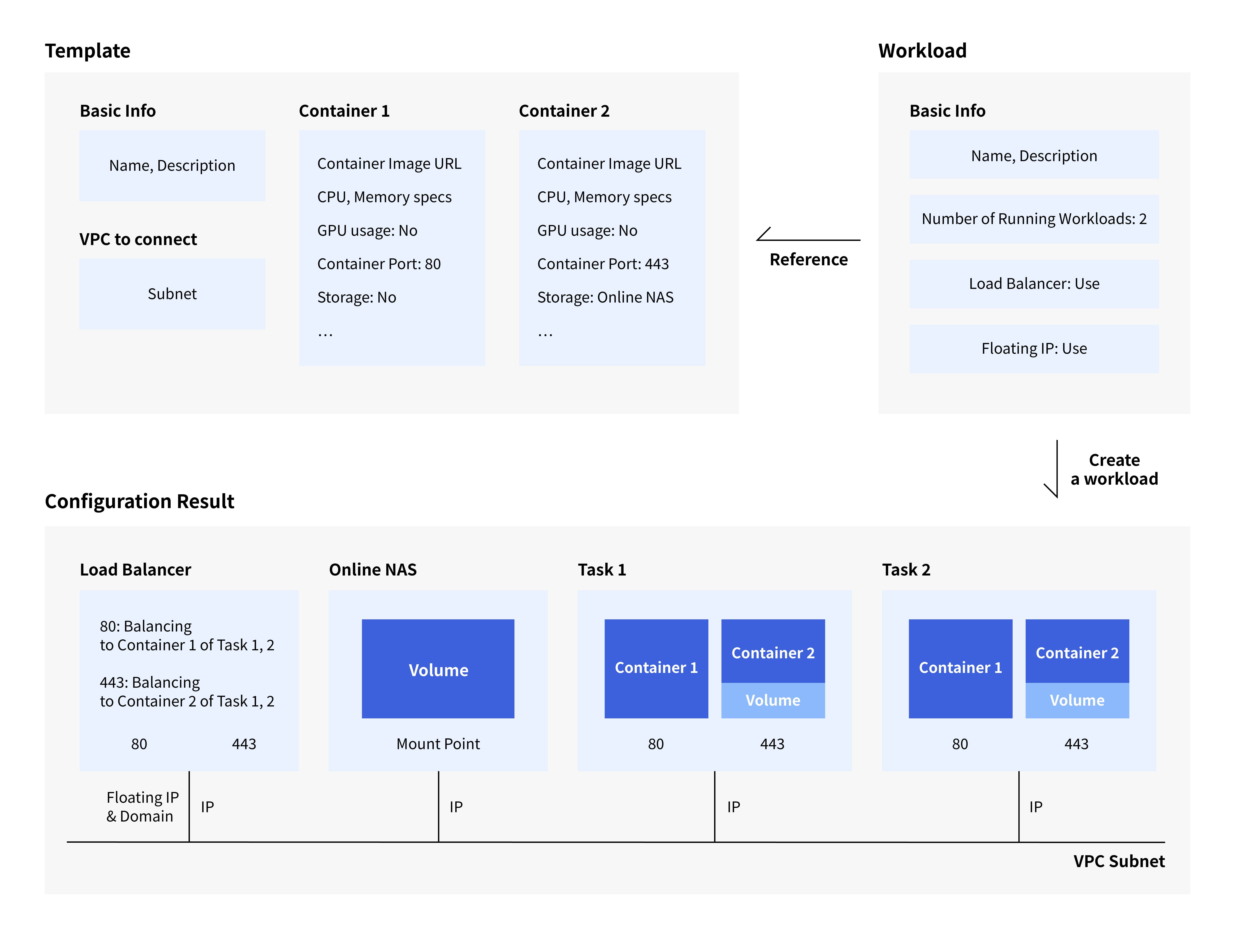
Template
Define which specification of the container to configure in Template.
Template describes the template name, description, VPC to connect to, and one or more container specifications.
Container specifications include a registry URL containing the Container image to run, resource specifications such as CPU, GPU, and Memory to be used, the port used by the container, and NAS storage to be connected.
Creating Template does not create a container. Template is a framework for creating workloads, and a container is created when creating the workload by using the Template.
With templates maintained, it is possible to create workloads and run containers only when necessary.
Workload
Define workload with reference to Template that describes container specifications.
Workload describes the referenced Template, the number of running workloads, whether the Load Balancer is enabled, and whether floating IP is enabled.
Image above shows the configuration result when you create an workload by setting the number of running workloads to 2 and defining the 2 container specifications in Template.
When creating a workload, the container defined in the Template is created under Task.
Task specifies the IP assigned from VPC subnet.
If you want to access the container port created in a place accessible to the VPC, you can access it with Task IP: container port.
The number of Tasks specified in the workload execution count will be executed. In the above example, two Tasks are created because 2 is specified in the example.
Load Balancer
When you set multiple containers to run in the workload and connect them to the load balancer, traffic load can be distributed to each container. If it is configured to use the floating IP, FIP is assigned to the load balancer and the domain is created.
Floating IP and Domain are not available if Internet Gateway is not connected to the specified VPC Subnet.